One of the most commonly used models for employee assessment is the 9 box grid. But, how does it work and why would you use it? While it can’t tell you everything, it can offer an insightful glance into employee performance.
At one point or another, every company needs to assess its talent pool to determine what’s working, what isn’t and what the future holds for its employees. Here’s how the 9 box grid works, and why you might want to consider using it today.
Download our guide to optimising your performance management processes.
Contents
What Is The 9 Box Grid?
How Do You Create A 9 Box Grid?
How Do You Use A 9 Box Grid?
Think Outside The 9 Box Grid
What Is The 9 Box Grid?
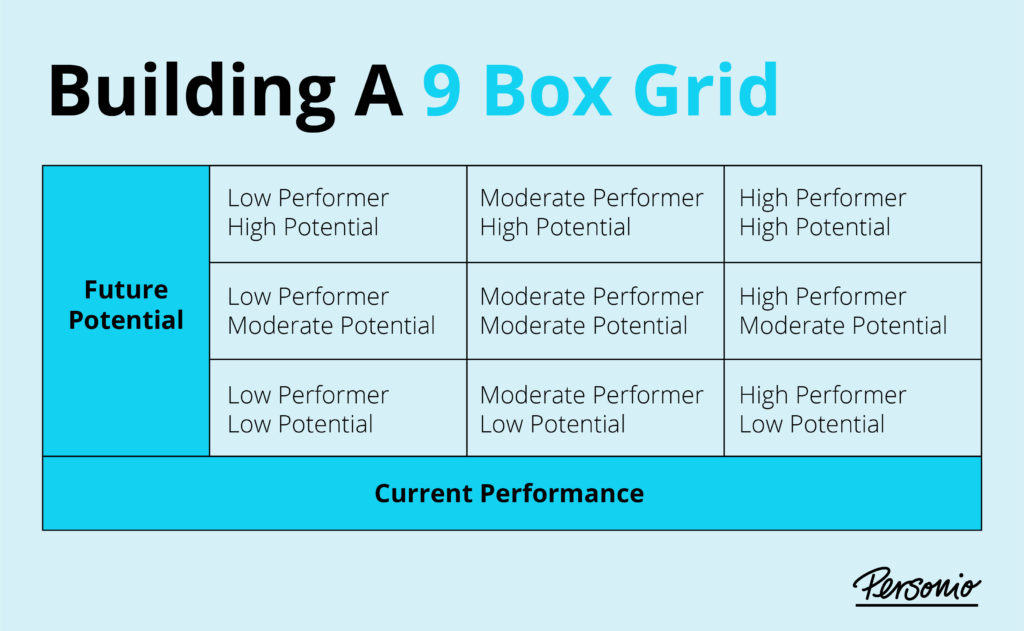
The 9 box grid is an employee assessment tool that divides and plots employees across 9 key data points. It is a grid-based system used to evaluate employees’ performance levels and potential for growth to fit them into each of these 9 segments.
Regularly used by those in HR and talent management roles, the 9 box grid is especially useful as a visual tool. This way, HR teams can see their entire workforce, or specific departments/functions/positions, at a glance and how they all come together.
What 9 ‘Boxes’ Make Up The 9 Box Grid?
The 9 box grid consists of the following groups, segments or boxes…
| Low performer with high potential | Moderate performer with high potential | High performer with high potential |
| Low performer with moderate potential | Moderate performer with moderate potential | High performer with moderate potential |
| Low performer with low potential | Moderate performer with low potential | High performer with low potential |
The Pros And Cons Of The 9 Box Grid
The 9 box grid is a semi-contentious assessment tool in the world of HR and people management. While some see it as a straightforward model, others see it as an outdated approach that’s too focused on labels.
But, let’s dive a bit deeper into both. The benefits and the drawbacks of the 9 box grid are as follows…
What Are The Benefits Of The 9 Box Grid?
It’s easy to use. With a simple and established structure, all you need to do is review your employee’s strengths and weaknesses to match them with the right box. The visual ease of the 9 box grid makes it easy for anyone new to the concept to catch on.
It increases transparency. The 9 box grid approach requires open and honest communication within the leadership team to evaluate each employees’ standing. These discussions can often help clarify leaders’ expectations and goals for the company.
It makes workforce planning easier. By using a 9 grid box, you’ll gain clarity on your employees’ strengths and can determine which employees have the potential for leadership or senior roles within the company. From there, you can ensure employees are getting the support and guidance they need to thrive.
On the other hand, if the grid helps you determine that an employee has high potential but low levels of performance, it can be the sign you need to work closely with the employee to increase their motivation and engagement.
What Are The Drawbacks Of The 9 Box Grid?
It uses unclear metrics. How do you measure someone’s potential? How do you differentiate potential from performance? Is an employee’s current performance an accurate reflection of how they could perform in the future?
If you want to effectively use the 9 box grid, determine how your team will measure potential and performance before you begin. Otherwise, the metrics themselves may be biased, unreliable or simply unusable (or not predictive of much).
Speaking of which, it invites bias. While employee assessments should be based on facts and figures, favouritism, bias and opinions can easily sway where an employee lands on the grid, therefore determining whether they move up in the company as well as the degree of support and recognition they receive.
When used effectively, the 9 box grid needs to be as objective as possible. Moreover, it needs to be based on objectivity, and there needs to be a clear reason and data point to back up the inclusion of workers as they are grouped out.
It confines employees to a specific label. Once an employee is placed in the grid, it can affect how the involved management team sees them. For example, if an employee is determined to be a low performer with low potential, that may negatively affect how the team treats and sees that employee from that point on.
Take Top Performers To New Heights
Build automated performance cycles to nurture your top talent.
How Do You Create A 9 Box Grid?
The 9 box grid is a simple three-by-three framework. To create your own, plot employees’ future potential on the y-axis (high potential, moderate potential, low potential) and their current performance on the x-axis (low performer, moderate performer, high performer).
While this is the standard and most straightforward form of the 9 box grid, many companies choose to customise each square to better define what each performance and potential level means to them.
Here’s how that could look:
- High performer with high potential: Employee meets and exceeds their responsibilities and goals, naturally and enthusiastically takes on leadership opportunities, and is prepared for new challenges.
- Moderate performer with moderate potential: Employee meets expectations for their role and has demonstrated a desire to lead, but must be developed and nurtured to reach the next level.
- Low performer with low potential: Employee does not meet expectations for their role and performance. They demonstrate a lack of motivation and alignment with the company’s vision.
Or, you can categorise each box in a more “approachable” way:
- A high performer with high potential is referred to as “A Star Employee.”
- A moderate performer with moderate potential is “A Core Player.”
- A low performer with low potential is “The Wrong Hire.”
How Do You Use A 9 Box Grid?
While the 9 box grid is a fairly simple method, it’s not always used effectively. Here’s how you can make this employee assessment tool work to its full potential:
Get Everyone On The Same Page
Review the 9 box grid structure and methodology with your team and confirm how you’re going to measure performance and potential. Consider:
- What benchmarks and criteria will qualify an employee’s performance or potential as low, moderate or high?
- What will your succession plan look like for employees who meet your high-performing, high-potential benchmarks?
- What will the next steps be for employees who are labelled as low performers or low potential?
Assess Each Employee’s Performance
Use each employee’s specific job description and responsibilities to create a customised framework for their assessment and get as specific as possible with their performance expectations.
For example, a basic framework for performance could be:
- Low: Does not meet the performance expectations set by job description or manager, did not meet last quarter’s sales goals, etc.
- Moderate: Employee meets performance expectations.
- High: Employee meets and exceeds performance expectations.
Assess The Individual Employee’s Potential
Potential is best measured not by an employee’s results but by their behaviour. An employee with high potential is typically one who is constantly developing their skills and is willing to learn and apply new knowledge.
- Have they already progressed in the company? If so, how?
- Does their current role allow them to progress further?
- Is there another role or department where they would be better suited?
- Has the employee indicated an interest in moving up in the company?
Place Employees On The Grid
From your assessment of their performance and potential, determine where the employee fits on the 9 box grid. This should be a collaborative exercise between management, HR and leadership to position the employee accurately. Encourage discussion to garner a well-rounded and unbiased view of the employee’s potential and performance.
Determine Next Steps
Once you’ve established where the employee lands on the grid, it’s time to assess what that means.
If they’re a high performer with high potential, what are their next career steps? Is there room for some kind of specific professional development? What are their career development goals?
These are the employees you want to build a career progression plan for — your star talent who will rise to the top with relative ease.
If you have a low performer with low potential, is it time to let them go? What roadblocks are they hitting in their work, and can they be overcome? If so, how?
For moderate performers, what can be done to help them reach the next level? Are they in the right position or department, or would their skills be better suited somewhere else within the organisation?
In some instances, those with high or moderate potential but low-performance levels are simply poorly placed within the company and can improve their performance in another, better-suited role or department.
Repeat The Process
Repeat the process above for each employee in your company. Once the evaluations are complete, take some time to review the outcomes with leadership.
Putting Performance Management In Focus
The key to nurturing your top talent: performance management. Download our guide on the matter today.
Think Outside The 9 Box Grid
The 9 box grid isn’t effective because it helps you match your employees with a certain label or box. The true value is found in the process and the discussions that stem from it.
While you shouldn’t use the 9 box grid to make the final decision on an employee, their potential, or their future within your company, it can be used as a starting point to establish their overall position and begin a productive conversation with management.
Assigning a label to an employee isn’t going to help them excel in the company. But the process can get the right people in a room together to clarify the company’s goals and future, collectively evaluate employees’ successes and bring the two together to put the organisation on track for excellence.
Help Develop
Your Top Talent